Why you need to know how to store fish
Fish contains the amino acid histidine. It is most abundant in salmon, tuna, mackerel, and herring. If stored improperly, microflora develops, which converts histidine into histamine with its enzymes. Increasing the level of this amine does not affect the taste properties. A person cannot determine the histamine content by smell or taste.
Histamine is normally found in the body and performs certain functions. However, in high doses it causes poisoning, clinical signs similar to allergies. Large amounts of histamine can lead to irreversible consequences.
The state regulates the maximum permissible concentrations of histamine, and inspection services constantly monitor the market. But even if the fish served on the store counter is benign in terms of histamine, improper storage leads to its accumulation.
It is important to know!
Heat treatment does not affect histamine levels.
How to determine the freshness of fish
Be sure to inspect the carcass before making a purchase. Pay special attention to the gills - they should be reddish in color. The eyes are bulging and clear. The structure of the meat is dense. The presence of damage, mucus, and stains on the surface of the scales is unacceptable. If you buy processed fish (smoked, marinated, dried), carefully inspect the product. There should be no damage to its surface.
Smell the fish - it should smell normal. If you buy a frozen product, inspect the glaze layer. The ice should be uniform and without damage. A layer that is too thick indicates re-freezing, which spoils the product. The presence of white spots indicates too long storage.
Storage conditions and periods according to GOST
Chilled
GOST for chilled fish stipulates that it should be stored at a temperature from 0 to -2 °C.
The deadlines are as follows:
| Fishing period | For large | For small fish (haddock, capelin, etc.) |
| from October to March | 12 days | 9 days |
| from April to September | 10 days | 7 days |
Pond fish packed without ice can be stored at a temperature not exceeding 6 °C for no more than 2 days.
Ice cream
Storage of frozen fish is regulated at a temperature not higher than -18 ᵒC.
Shelf life of frozen product according to GOST
All other uncut fish are stored for no more than 4 months, cut - 3 months.
If the storage temperature is not higher than -25 °C, then the period is increased by 2 months.
Hot smoked
For this type of product, GOST regulates the following terms:
• at a temperature of 2–6 °C – no more than 48 hours; • from -2 to 2 °C – 72 hours; • at -18 °C – 30 days.
Cold smoked
For such a product, temperature parameters are defined from -5 to 0 °C, and the period is no more than 2 months. At the same temperature, vacuum-packed fish can be stored for no more than 20 days. At temperatures not higher than -8 °C, the period increases to 30 days.
If the fish is from inland waters, then store it for up to 40 days at a temperature of -2 to 1 °C.
Salty
If fish is stored in barrels with brine (7% salt solution) at a temperature from -8 to 4 ᵒC, then the terms are as follows:
• lightly salted – 4 months; • medium salting – 6 months; • strong salting – 9 months.
We recommend reading: Herring in the refrigerator: simple recipes for long-term storage.
What product can be kept in the refrigerator?
The issue of storage in a refrigerator should be decided taking into account the temperature distribution in it. It should be taken into account that on the coldest shelves the temperature is maintained in the range of 0-3 degrees, and in the lower part 2-6 degrees. This temperature is not enough for long-term storage of most types of fish products.
The average shelf life is 2 days. Within this period, you can keep any fish in the refrigerator, except frozen. At these temperatures, ice begins to melt and the product begins to defrost. It will not be possible to store live fish in the refrigerator.
How to choose fresh
To avoid mistakes, buy only live fish. Even a child can recognize her - she moves her tail, fins, and jaws. If the fish is dead (not alive), refuse to purchase.
Of course, there are a number of signs that determine how long ago the fish was caught. But the current environmental situation is so bad that even a laboratory is sometimes unable to determine its freshness.
If the fish shows no signs of vital activity, then pay attention to:
- Appearance. The surface must be clean. The scales are held tightly, intact and without damage. The consistency is dense (don’t be afraid to press the carcass with your finger).
- Gills. The rich red color and lack of odor indicate freshness. Some species have pink gills and a specific smell - this is also the norm. If the reservoir is polluted, then this indicator can be ignored.
- Smell. Specific fishy, without any extraneous notes. A faint smell of sludge is acceptable. If it is sour or unpleasant, the fish is not fresh.
The importance of water when transporting fish
Since water is the habitat of fish, it plays an important role during transportation. As mentioned earlier, temperature and oxygen saturation must be taken into account during transportation.
The fish are moved to specialized containers that regulate deviations from the norm. In this case, the fish endures transportation without stress.
Time does not stand still and now water is not required for transportation; if the travel time does not exceed four hours, the fish is put into a state of sleep, thereby slowing down the internal processes of life. This method does not harm the fish’s body.
How to store raw food: terms, conditions, packaging
At home, store fish only in the refrigerator and for no more than a day. You don’t know how long it was stored before it came into your kitchen. Don't risk your health.
How to prepare (does it need to be gutted?)
The fish should go into the refrigerator gutted. Ideally: brought, gutted, placed in the refrigerator, or better yet, cooked immediately.
In a refrigerator
Bags and paper are already a thing of the past. A plastic container is ideal. In this case, there is no need to choose a place and look at the “neighbors” on the shelf.
When figuring out at what temperature chilled and gutted fish is stored, it should be taken into account that a household refrigerator cannot create 2 °C. At higher temperatures it is dangerous to keep the product for a long time. If the carcass is cut into portions and washed, then it can be stored for no more than 24 hours.
There is no way to cook fish within 24 hours - put it in the freezer!
In the freezer
For freezing, the product can be wrapped in plastic bags or paper, but it is better to put it in a container. Only gutted fish should be frozen.
If the carcass is divided into portions, then it is advisable to pack each separately. In this case, you can remove only the part that is necessary for cooking.
The freezer compartment of a home refrigerator does not always provide -18 °C. Therefore, when deciding how long fish can be stored in a household freezer, you should limit yourself to 2 months.
After defrosting
In order for defrosting to be successful, fish from the freezer is placed in the refrigerator and not allowed to completely defrost. The preparation of the dish begins when it is still slightly frozen and not a single microbe has begun to multiply.
Note to the hostess
Fish should not be re-frozen - it will lose its integrity during subsequent cooking.
Without a refrigerator, on the road
Nowadays there are thermal bags and thermal bags, so the transportation process is easier. If you don’t have a bag or package, you can use ice or plastic bottles with frozen water. But remember, when the ice completely melts, the fish carcass begins to heat up and microorganisms multiply - this is dangerous.
If safety conditions cannot be ensured, refuse transportation. The product will be spoiled.
We recommend reading: Food thermal bags: 5 uses you didn’t know about.
In a vacuum
If the fish is vacuum packed, there is only one piece of advice - follow the instructions on the label. Only the manufacturer knows how and for how long such a product can be stored.
The duration of storage of a product in a vacuum depends on the preservatives with which it is treated and on the conditions during packaging
How to know if a product is expired
For each type of fish product there are signs that it is no longer suitable for consumption:
| View | Subspecies | Signs |
| Fresh | caught | Unnatural coloring of the skin, mechanical damage, a thick layer of mucus on the surface of the body, a specific smell with a putrid tint, dull sunken eyes, a swollen belly, flabby body consistency, the color of the gills is any except red (for chilled ones it is also dark red or pink). |
| Chilled | ||
| Frozen | Yellowing, unpleasant odor, dull skin during defrosting and secondary freezing, deformation of the carcass body. | |
| Cooked | Smoked | Unpleasant sour smell, change in color and taste of the product, the appearance of mold, slippery coating. |
| Dried | The appearance of an atypical odor, mold, change in color and taste. | |
| Dried | ||
| Salty | It smells rotten, becomes slimy and loose to the touch, tastes unpleasant, and mold appears. | |
| Fried | The appearance of an unpleasant odor, mold deposits, changes in taste and consistency. |
How to store live
Live fish is an ideal product. However, if caught in polluted waters, it can be dangerous.
If the fish is alive, then expiration dates are not established even by GOST. However, the conditions of transportation and sale are regulated. Particular attention is paid to the fact that:
- Live fish should be stored in water with a temperature difference between the tank and the reservoir of no more than 4 °C;
- the aquatic system must be aerated and supplied with running water.
Do you know that…
The difference between live and dead fish is that the former shows signs of vital activity and its price is correspondingly higher.
At home
Live fish are stored in water. In this case, the liquid must be completely changed every day.
During the cold season, low water temperatures can be maintained by nature itself. In summer, it is better to lower the container with fish into the basement.
Fishing
Experienced fishermen, in order to deliver the fish home fresh, cover it with nettles. This is a dubious method. At high ambient temperatures, nettle does not help.
If there is a lot of fish and the journey is long, it must be gutted at the fishing site, washed and sprinkled with salt.
Specialized vehicles
An important point in transportation is not only proper inspection of the fish, but also a thorough approach to preparing transport. Before setting off, the car must undergo a full technical inspection to avoid breakdowns along the way. The owner must select a car with a tank size suitable for transportation.
It is also important to check whether the tank has been disinfected and washed with running water. Afterwards, the container is filled with water in which the fish was previously kept.
It is important that the water should not contain vegetation. The reservoir must provide oxygen supply and thermoregulation.
It is recommended to transport fish at night or early in the morning. While on the road, the driver needs to check whether there are any disturbances in the oxygen supply or thermoregulation.
A significant deviation from the norm can lead to serious consequences. In a new body of water, the fish may experience stress at first and undergo adaptation. During this period, constant supervision by a specialist is necessary.
How to store the finished product: terms, conditions, containers
Even if you bought fresh fish and cooked it quickly, the shelf life of the dish is not long.
The time allotted for consuming a ready-made fish dish is literally measured in hours due to the rapid development of microflora
Boiled, baked, fried
Any cooked and uneaten fish, once cooled, should be placed in a container and transferred to the refrigerator. Shelf life 12 hours. If you don't eat it, freeze it.
If the fish soup has been cooked, do not pour it into a container and do not remove the fish. Place the container in which the dish was prepared in the refrigerator. After storing in the refrigerator, you need to bring it to a boil and only then start eating.
Smoked
A cold or hot smoked product brought home must be eaten within 48 hours. A household refrigerator does not allow you to store smoked fish for longer.
If there is a lot of fish, wrap it in two plastic bags or put it in a container and put it in the freezer. If frozen, the product can be stored for up to 30 days.
It is important to know!
Modern smoking means new technologies. The fish is soaked in a special solution - “liquid smoke” - and dried. This product should not be given to children and people with chronic diseases.
Sun-dried, dried
When buying such fish, give preference only to labeled products. The manufacturer himself determines the shelf life and indicates it on the packaging. Conditions of detention are also described. After opening the package, the product must be eaten.
Storage of dried fish depends on the amount of fat in the product. This is difficult to determine visually. The less fatty the fish, the longer its shelf life:
- fatty (more than 10%) can only be stored in the freezer at -18 °C for up to 5 months;
- non-greasy - in a dark, dry, ventilated area for up to 2 months.
Dried in the freezer can be stored for up to 5 months, at a temperature of 0 to 6 °C - up to two.
To prevent dried fish from drying out, you can wrap it in parchment, put it in a container with a tight-fitting lid and put it in a dark, cool place
Salty
Storing salted fish depends on the salt content in it. The saltier the product, the longer it can be stored. However, production times of 4, 6, 9 months apply only to large freezers.
At home, salted fish can be:
- place in a 7% salt solution and refrigerate for up to 10 days (in this case, it does not matter how much salt was there before);
- wrap it in a plastic bag and put it in the freezer for a month;
- cut into portions (without bones), place tightly in a container, fill with sunflower oil to the top and store in the refrigerator for up to 10 days, in the freezer for up to a month.
Tip of the day
Red fish is stored as indicated by the manufacturer on the label. Only he knows the preservatives with which the product was processed. If there are no instructions, place in the freezer for no more than a month.
Transportation rules
Not all fish can be transported and loaded into specialized containers. Fish that are infected or suffer from certain pathologies are not allowed for transportation. To admit fish for transportation, a special examination is carried out to confirm the health of the fish and its readiness for transportation.
- Fish that have obvious damage to the body or do not show their usual activity for transportation are not allowed; they may not survive the long journey.
- Veterinarians recommend not feeding the fish the day before transportation, as due to the long journey, they can be poisoned by their own waste.
- The water in containers must be clean and free of any vegetation.
Signs of a spoiled product and what to do with it
If the fish seems suspicious, refuse to purchase, even if the expiration date has not expired. If doubt arises during storage at home, discard the product. Remember that they are easy to poison.
Signs of the onset of damage may include changes:
- colors;
- consistency;
- smell.
Do you know that…
Some peoples prefer to eat fish “with flavor” and feel good at the same time. This is not our option. The body adapts (produces enzymes) to the lifestyle over the years, and this is fixed at the genetic level. If such a dish is not a traditional food product for you, it is better not to risk it.
Short distance transportation
Such transportation is relevant for moving live fish from one farm to another. Nearby transportation is considered to be transportation within the region, the distance of which is no more than ten kilometers. Live fish is also transported for delivery to the nearest retail outlets.
- Small containers can be used to transport live fish over short distances. For example, buckets with a lid, but it's not that simple. Buckets must be securely fixed so that during transportation they do not move or overturn, thereby harming the fish.
- It is important to make holes in the lid to allow oxygen to enter. If the fish falls out of the container during transportation, it must be separated from the rest of the fish, the mucous membrane of the fish is damaged, and within a few days it will die.
The influence of cooling procedures on product quality
According to the technology, only live fish or fish that have just fallen asleep are subjected to cooling. The period for which chilled fish can be stored depends on the degree of thermal conductivity of certain types. It is this indicator that affects how long a fish carcass of a particular type can remain refrigerated without compromising its quality. At the same time, there is a difference in the duration of cooling measures and the final shelf life. They depend on the following factors:
- carcass fat content;
- ambient temperature indicators during cooling;
- size of the individual.
During the cooling event, the tissue density increases. At the same time, the blood becomes thicker, and the weight of the carcass decreases, as excess moisture evaporates from the surface of the fish. The higher the humidity in the room where the product is cooled, and the lower its fat content, the more mass is lost. There is also a dependence on the method of cooling - if on ice, then the weight decreases more, and when in a liquid medium, the weight decreases less.
How does the cooling process occur?
Based on regulatory provisions, chilled fish specimens when interacting with ice are preserved for 7-12 days . It all depends on the seasonal catch and its size.
Unfortunately, the established time frame does not make it possible to fully provide the population of the Russian Federation, located at a distance from fishing grounds, with chilled products.
Such restrictions do not allow the use of industrial processing of this product.
The existing problem was resolved by a team of Russian specialists.
They proposed their own version of improving the cooling process, increasing the time savings to 25 days at temperatures from -1 to -3 degrees Celsius.
The basis was the food addition of multifunctional compounds “Varex-7” and table salt with certain structural forms of ice.
During testing, this food complex proved the necessity of its presence.
Small scaly pieces of ice come into close contact with the fish without creating large air spaces. They stop the proliferation of harmful microbes, bacteria, enzymes as much as possible, and also temporarily localize lipid oxidation.
A varied concentration of additions allows the ice to regulate the temperature of the chilled product. the highest quality is maintained throughout the entire storage time .
Today this process has become even more advanced. a cooling gel using the Varex-7 complex and table salt .
The frozen solution completely covers the fish, creating an outer cocoon for it.
Then it penetrates into the internal cavity , enveloping the organs and cooling the entire anatomical structure.
This makes it possible to quickly reduce temperature values close to cryoscopic ones and maintain them until they reach the customer.
Cooling gel makes it possible to increase the saving time up to 40 days .
From this article you will learn how to properly store honey.
Cold processing and storage of fish and fish products at low temperatures
Cold processing and storage of fish and fish products at low temperatures in modern conditions is one of the promising methods of preservation, which allows one to maintain the original high quality of the product for a long time and transport it from production sites to the consumer.
When frozen, the water contained in fish passes from a liquid to a solid state, therefore the vital activity of microflora and enzymatic processes cease.
For most bacteria found in fish, the optimal development temperature is 25-35 ° C, but some types of microbes do not stop vital activity at a temperature of minus 3 ° C.
Cold canning of fish is divided into the following main methods: cooling, freezing (hypothermia), freezing and thawing. Each of them is characterized by certain parameters, established technological requirements and standards.
Cooling is the process of lowering the temperature of the fish from its initial temperature to close to the cryoscopic tissue sap point (the temperature at which the water in the fish tissue changes from a liquid to a solid state). In freshwater fish, the freezing temperature ranges from 0.5 to -0.9 °C, and in marine fish - from 1 ° to 1.6 °C. Therefore, the temperature of chilled freshwater fish should not be lower than 1 °C, and for sea fish -2 °C. At the same time, the maximum temperature should not exceed 5 °C. Thus, fish is considered chilled if it has a temperature in the thickness of the meat at the spine from -1 to +5 °C.
In chilled fish, the activity of microflora and enzymes slows down, so it can be stored for a limited time. This depends on a number of factors. Fish should be cooled immediately after catching, stored at a constant temperature ranging from 0 to -1 ° C, and sanitary and hygienic conditions must be observed. Chilled fish can be stored for several days longer if its entrails and gills are first removed. The faster the fish is cooled and the lower the temperature, the slower the post-mortem changes occur in it.
The contamination of chilled fish with microflora largely depends on the quality of processing, the cleanliness of the container, room, etc. Fish cooled in compliance with sanitary standards is stored for up to 12 days, and if they are violated - about 5 days.
Before cooling, the fish is washed in clean cold water, sorted by size, if necessary, cut up and placed in containers: small ones - in bulk in layers, and large ones - in one or two rows, back up.
There are several accepted methods for cooling fish, the most common of which are using ice and a solution of table salt. Using cold air as a cooling medium is less advisable, since the process proceeds more slowly and the surface of the fish dries out, resulting in a deterioration in presentation.
Cooling fish with ice.
Finely crushed ice is used, which has a sufficiently large cooling surface and, therefore, quickly reduces the body temperature of the fish. Pour it onto the bottom of the container and between the rows of fish. The method is simple and accessible, although it also has certain disadvantages: the fish cools unevenly, at a relatively low speed and is greatly deformed; there is a loss of nutrients with leaking muscle juice.
For the northern regions of the country and in the cold season, the amount of ice should be 40% of the weight of the fish, in warm times - 75, in spring and autumn - 45-60%. Packaged fish are quickly sent to the retail chain. The duration of cooling fish with ice depends mainly on the size of the fish, the dosage of ice and the degree of its crushing. The total height of the layer of fish in the container during storage and transportation should not exceed 30-40 cm.
Liquid cooling.
A 2-3% solution of table salt or sea water is used as a cooling liquid, the osmotic pressure of which is approximately equal to muscle juice, so the salt does not penetrate into the fish. This method has some advantages compared to cooling in ice: the fish is quickly and evenly cooled to the cryoscopic point, does not deform, and takes up less production space.
Fish cooled in a liquid medium is used mainly for salting, since part of the salt remaining on the surface of the product penetrates under the skin and stimulates fat oxidation during long-term storage. The temperature of the chilled water should be from 0 to -2 ° C in a ratio of 1:1 or 2:1 to fish. The cooling process works better if you add ice to cold water.
The duration of cooling in a liquid medium depends on the size of the fish, water temperature and ranges from several minutes to 3 hours or more. It is impossible to store fish in a liquid medium for a long time, especially with thin skin (no more than 4-5 hours), since swelling occurs and its weight increases by 11-12%, and nutritionally valuable substances are removed from the tissues.
To increase the cooling efficiency, it is advisable to add antibiotics (mainly biomycin) or antiseptics (calcium or sodium hypochloride, hydrogen peroxide, etc.) to the liquid, as well as to ice. These substances slightly penetrate deep into the muscle tissue, do not affect the taste, color and smell of the fish and are easily washed off with water when washed, while at the same time inhibiting the development of most types of bacteria.
Cooling with a mixture of ice and salt is acceptable in cases where the fish is intended for salting. Typically, at an air temperature of 5-20 ° C, the mixture is prepared in a ratio of 80% ice mass and 20% salt. When the ice melts, a temperature of -8 -12 °C is obtained, which ensures rapid cooling of the fish. At the same time, the salt partially penetrates the fish, giving it a salty taste.
Air cooling . The fish is placed in boxes and must be hermetically covered with a tarpaulin or film, which reduces the degree of drying and darkening of its surface. Cooling in air takes a longer time and, depending on the size of the fish, lasts 4-10 hours. When cooling in air with a temperature below -2 ° C, it is necessary to prevent it from overcooling. Dry ice (solid carbon dioxide) is sometimes used as a source of cold, but its use is limited by its relatively high cost.
Storage and transportation of chilled fish. To store chilled fish, they mainly use wooden boxes or barrels, as well as boxes made of polymer materials. Storage temperature is from +5 to -1 °C (preferably +1 -1 °C) and relative humidity is 95-98%. In markets and warehouses, uncut fish are stored for 8-9 days, and gutted fish for up to 12 days. Holes are made in the bottom of boxes and barrels to drain water from melted ice. Fish of the same type, size and cutting method are placed in a packaging unit.
The maximum shelf life of chilled fish in the retail chain in refrigerated chambers at temperatures from -1 to +2 °C is no more than 2 days, and in boxes with fish sprinkled with ice at temperatures from 2 to 4 °C - no more than 24 hours. Transported chilled fish in isothermal transport (road, water, rail), in which the temperature is maintained at a level from +5 to -1°C.
When storing chilled fish, there may be a loss in its weight, depending on storage conditions, etc. So, when cooling mirror carp, its weight increases by 3%. When dead fish are cooled, their weight decreases. Shrinkage rates for chilled fish in the retail chain are set depending on the zone (1 and 2) at 0.63-0.68%. When transporting in the cold period over a distance of 25 km, losses are 0.09%, 50 km - 0.12 and more than 50 km - 0.15%, in the warm period, 0.12, 0.15 and 0.18%, respectively.
When storing chilled fish in warehouses and rural retail trade for 2 days, losses amount to 0.13-0.15%.
Requirements for the quality of chilled fish.
Chilled fish must be unbeaten (scales may be broken without damaging the skin). The surface of the fish is clean, the color is natural (depending on the species), the gills are from dark red to pink, the consistency of the muscles is dense (slightly weakened, but not flabby, is allowed for sale). For fresh fish, foreign odors that discredit the product are not allowed. When sold, there may be a slight sour smell in the gills, which can be easily removed by washing with water. Fish must be cut according to accepted rules.
The main defects of chilled fish are mechanical damage, weakening of consistency, sour or putrid odor in the gills, the presence of mucus on the surface, rupture of the walls of the abdominal cavity (lopanets) as a result of tissue autolysis or mechanical impact due to violation of storage and transportation conditions. Defects in chilled fish occur mainly due to autolysis and microorganisms.
Rules for sampling and external inspection of chilled fish (GOST 7631-55). To study and assess the quality of chilled fish, about 5% of all containers in a given batch are opened and inspected. For organoleptic examination, an average sample (several specimens of fish) is taken from different places in the opened container. During an external examination, the size, consistency of the meat is determined (the fleshy parts are probed), temperature (measured with a thermometer in the depths of the thick part of the body), smell (the body is pierced with a knife or hairpin between the head and dorsal fins, places of wounds and mechanical damage, entrails through the anus, growths etc.).
The color of fish meat is determined by a cross-section in the thickest part of the body. For laboratory research, an average sample is taken depending on the weight of individual fish specimens: weighing up to 100 g - no more than 1 kg, up to 2 kg - 1-2 fish, 2-5 kg - halves of 1-2 specimens, more than 5 kg - individual transverse pieces 3-4 cm wide from the head, middle and tail parts weighing about 500 g.
The good quality of chilled fish (freshness or physicochemical properties) is determined according to GOST 7636-55. Small fish are ground whole without cutting, while large ones have their spine and, if possible, ribs removed.
Freezing fish. To obtain frozen (supercooled) fish, it is cooled to a temperature in the deep layers of the body from -1 to -3°C, which allows the shelf life to be increased to 20-30 days. Freezing leads to partial freezing (shrinkage) of moisture and deformation of tissues by the resulting ice crystals. The most optimal final temperature for frozen fish is 2 °C. In this case, the shelf life of the fish is extended by 8-10 days compared to chilled fish, and its quality is practically no different from the latter, so it can be sold as fresh fish. However, to store frozen fish, it is necessary to observe the temperature regime. An increase in temperature above the cryoscopic temperature is accompanied by defrosting and a fairly rapid deterioration in the quality of fish. Lowering the temperature below -3°C also reduces the quality of the fish. Temperature fluctuations during storage and transportation of supercooled fish are not allowed.
The time for transporting frozen fish at a temperature of -1... -3°C in refrigerated transport should not exceed 10 days. Frozen fish are assessed in the same way as chilled fish.
To increase shelf life, chilled or frozen fish can be additionally treated with carbon dioxide. In this case, the viability of many microorganisms is suppressed, including psychrophilic (cold-resistant) bacteria and especially molds. Chilled fish can be stored for 50-60 days in an atmosphere containing up to 10% carbon dioxide at a temperature of 0 ° C, with no changes in smell, taste, consistency, and fat oxidation slows down. To use carbon dioxide, you must have a sealed chamber or container.
Freezing fish. Ice cream is a fish whose temperature in the deep layers of muscles is brought to -6 °C or lower. Freezing is the most common method of preserving fish, allowing it to be stored for a long time with a relatively small decrease in quality. In this case, the bulk of the water contained in the tissues turns into a solid state, and therefore the vital activity of microorganisms practically stops, and enzymatic, chemical and physical processes slow down sharply. At a temperature of -2 °C, about 49% of the moisture in freshwater fish freezes, at -8 °C - about 76%, at -14 °C - about 85%, and only at 60 °C does all the water turn into a solid state. In the latter case, the volume of the fish increases by 8-10%, which leads to tissue destruction.
The nature of the formation of ice crystals in fish tissues is significantly influenced by the speed of the freezing process. With slow freezing (temperature - 7-12 ° C), few crystallization centers are formed in the muscles, as a result, large ice crystals form between the muscles. As the crystals freeze, the size of the crystals increases, pressure on muscle fibers and cells increases, and, as a result, tissue destruction occurs, compression of muscle fibers, dehydration of protein colloids, and partial denaturation of proteins (especially myosin).
When fish is defrosted, colloidal tissue solutions lose their ability to absorb water. This causes the meat to become tough, dry, sometimes coarse-fibrous and watery, and insufficiently aromatic and tasty.
With rapid freezing at temperatures from -18 to -35 °C and constant low storage temperatures, the structure of fish tissue changes. In this case, more centers of water crystallization appear, which are located both between the fibers and inside and outside the cells. The concentration of salts in cells and intercellular spaces changes slowly, proteins are denatured slightly, they retain a greater ability to swell. When defrosting fish, the amount of leaking meat juice decreases, and the original muscle structure is almost completely restored.
Fast freezing is more economical than slow freezing and takes less time. The freezing speed increases by 20 times if the process is carried out in a liquid medium, and by 3-4 times if the air circulation speed is increased. The speed of freezing depends on the size of the fish. In practice, fish is considered to be quickly thawed if the temperature inside the muscles drops to -6 °C for no more than 2 hours.
Particularly significant structural changes in fish occur when it is re-frozen, after thawing, or when there are sharp fluctuations in temperature and humidity during storage. Such fish is considered a product of questionable quality and freshness; its surface becomes dull, frost appears on it, and the color and consistency of the muscles change. It can be a source of food poisoning. Therefore, when assessing its quality, it is necessary to conduct thorough laboratory tests.
Methods for freezing fish. Fish is frozen by natural (ice-salted mixture) and artificial cold obtained by machine (ammonia cooling).
Freezing with natural cold.
It is used in areas with cold winters, in places where fish are caught (on ice), when the air temperature does not exceed -10 °C (preferably -15 °C and windy weather). At higher temperatures, the fish freezes slowly, its mass decreases (dries out), and the surface darkens. Fish frozen using this method is of high quality; it is called “dust” or “spray”. Such a fish has a half-open mouth, bulging eyes, protruding fins and gill covers, bright red gills, a generally curved body, a shiny surface, and a dark red stripe on the underside of the head. In frozen dead fish or frozen at an insufficiently low natural temperature, the gill covers and fins are pressed down, the skin is dull, and the eyes are sunken to the level of the orbits.
To freeze fish with natural cold during winter fishing, select an area without snow and free from wind. Large fish are laid out on the platform one by one and turned over periodically. Small fish are laid in a layer 12-15 cm thick. After freezing, the fish are tightly stacked and covered with tarpaulin, film or burlap; during long-term storage, they are covered with snow 1.5-2 m thick, after compaction, they are watered with water and covered with insulating material.
Depending on the type of fish and freezing conditions, natural loss is 2-6%.
Ice-salt freezing. When added to ice, 14% of table salt reaches a temperature of -9 ° C, 16% - up to - 10 ° C, 18% - up to -12 ° C, 24% - up to -17 ° C, 30% - up to -20 ° C . In the mixture, ice melts and salt dissolves in water, while heat is absorbed.
Fish is frozen in the following ways:
dry contact - the fish are placed in boxes and covered in layers with an ice-salt mixture. To reduce deformation and salting, the fish is separated from the ice-salt mixture using galvanized sheet iron. The brine drains as it forms;
wet freezing - the brine is not removed from the sealed container, but is left with the fish until it is completely frozen. Fish frozen in this way is, as a rule, of low quality, its surface layer is salted, becomes soft, dull, the muscles are dark, the gills are light, and the fish is often deformed. The most significant disadvantage of the ice-salt method is slow freezing, which makes it possible to obtain fish at a temperature of -8-10°C. Weight loss with this method, depending on the type of fish, is 0.6-3%.
Brine freezing. The fish is kept in a solution of table salt at a temperature of -16-20 °C using contact and non-contact methods. At first, it is loaded into metal containers, placed in cold brine or irrigated with it. With this kind of freezing, the same disadvantages are noted as with ice-salt freezing, with the exception of deformation of the fish.
With the non-contact method, the fish is placed in brine in sealed containers, resulting in a higher quality product.
Ice-salt and brine freezing are mainly used in cases where it is impossible to use other methods.
Air freezing is carried out in quick-freezing devices and chambers using ammonia cooling at temperatures from -23 to -35 ° C and below, with intense air circulation and relative humidity of 90-95%. Small fish are frozen on galvanized iron sheets in a layer of 13-15 cm, large fish are laid out in one row without touching each other or hung.
Thanks to rapid freezing, high-quality fish are obtained; they have a natural color, bright red gills, light, bulging eyes, fins and gills pressed to the body.
Glazing of frozen fish. During long-term storage, the quality of frozen fish deteriorates mainly as a result of surface drying and oxidation (rancidity) of fat. To slow down these processes, frozen fish is glazed, that is, a thin ice shell is created over its entire surface, which performs a protective function.
Storing frozen fish.
Almost all types of fish are prepared and sold in frozen form. To obtain high quality fish, the maximum temperature in the thickness of the muscles is regulated. It should be no higher than -18 °C with air freezing, -12 °C with brine and -6 °C with the natural method. The temperature regime is constant with fluctuations of ±0.5 °C. When loading and unloading chambers, a temperature increase of 3-4 °C is allowed. Relative air humidity in the chambers is 94–98% ± 1%.
The shelf life of frozen fish depends on the temperature and preservation method. Fish frozen by contact brine and ice-salt methods can be stored for no more than a month, glazed - 7 months, with air freezing - 4-6 months.
To store frozen fish, boxes, boxes, barrels, matting bales, bags, etc. are used. The container must be durable, clean, and free of foreign odors. The inside of the wooden container is lined with wrapping paper. Particularly valuable varieties of fish (whitefish, nelma, etc.) are wrapped individually in parchment. Each package contains fish of the same variety, type, size, cutting and freezing method.
To reduce quantitative and qualitative changes, fish during long-term storage is covered with a tarpaulin, film or other insulating material. During storage, it is recommended to periodically inspect frozen fish for the presence of mold or rust and, if necessary, make a decision on sale.
Changes in frozen fish. During the process of freezing and storage, physical and physicochemical changes occur in fish, as a result of which its quality deteriorates. With physical changes, color, recrystallization and evaporation (freezing) of moisture are disrupted. At temperatures above -18 ° C, a certain part of the water remains in a liquid state, it evaporates from the tissues, and the ice sublimates. As a result, fish shrinks on average 0.1-0.4% per month, depending on its type, air humidity, freezing method, packaging, etc.
During long-term storage, muscles acquire a dry, hard, fibrous consistency, the aroma and taste weaken, and the digestibility of meat decreases. The subcutaneous layer of the fish becomes spongy, severely dehydrated, not only sublimation processes occur in it, but also when air oxygen penetrates, the oxidative processes of fat are activated. Fish proteins, especially in the surface layers, undergo denaturation, resulting in a decrease in the water-holding capacity of the muscles. When air humidity fluctuates, frost forms on the surface of the fish.
The fine-crystalline structure of ice, formed during the rapid freezing of fish in the presence of fluctuations in temperature and humidity in the storage chamber, constantly turns into a coarse-crystalline structure. Repeated temperature fluctuations during fish storage, even within 1 °C, lead to recrystallization, and the resulting crystals change the histological structure of tissues and deteriorate the quality of the product. Due to different optical refraction of crystals of different sizes and the destruction of coloring substances, the color of the meat changes when cut (becomes grayer).
These processes lead to the appearance of a specific and relatively common persistent defect in long-term frozen fish - an “old smell”, especially noticeable when processed at high temperatures.
Complex chemical and biochemical processes occurring in frozen fish are determined by the activity of enzymes and the oxidative processes of fats.
At a temperature of -12 °C and below, the development of microorganisms in fish practically stops, although if the sanitary and hygienic regime is violated, various types of mold may appear on its surface. Enzymatic processes in such fish are reduced, and, consequently, protein breakdown products constantly accumulate in the fish: amino acids, trimethylamine, volatile nitrogen bases and others, which serves as a sign of fish spoilage. The redistribution of moisture in tissues during freezing contributes to the denaturation of proteins, resulting in irreversible changes in the structure of protein molecules and colloidal solutions in fish meat. The moisture-holding capacity of the muscles deteriorates; a significant amount of moisture with the components dissolved in it drains during defrosting, which causes high humidity in the defrosted fish.
The degree of protein denaturation depends on the temperature and duration of storage of frozen fish. With increasing temperature and especially with its fluctuations and increasing shelf life, the amount of denatured protein increases.
A significant role in frozen fish is played by oxidative processes, which are activated by enzymes in tissues, elevated storage temperatures and free contact with atmospheric oxygen. Fish oil gradually breaks down and oxidizes, which is accompanied by the accumulation of products that impair the taste, smell and color of the fish. These processes are especially noticeable during the storage of fatty fish containing many highly unsaturated fatty acids.
Frozen fish stored at temperatures above -18 °C and with abundant access to atmospheric oxygen develops a “rust” defect.
Assessing the quality of frozen fish. The quality of frozen fish largely depends on the initial state of the raw fish (live, fresh, frozen, chilled, etc.).
Freezing largely masks the initial signs of spoilage of fish, so its quality should be assessed both in the frozen and thawed state.
A fish that has just fallen asleep and then immediately frozen has the following signs: the eyes are slightly sunken, the fins fit tightly to the body, the mouth is slightly open, the color is light. Fish with pronounced signs of autolysis is dark in color, its surface is dull, and it has a weakened muscle consistency after thawing. Such fish are considered non-standard and are not allowed for sale.
If defrosted fish is in a structureless jelly-like state with positive data on the degree of freshness, then the presence of parasites should be assumed in the fish.
A serious defect of frozen fish is drying out of the outer layer, spongy structure and oxidation of fat. An unpleasant smell of “old fish” is noted in such fish. This defect is most often found in fish that contain a lot of water in their tissues (pike, carp, roach, etc.).
When assessing the quality of fatty fish, special attention is paid to the condition of the fat and the presence of yellowing as a result of oxidation. Initially, yellowing is noted on the surface, then gradually penetrates under the skin and into the muscles, giving the product an unpleasant taste. The increased salt content in fish frozen in brine accelerates the development of oxidation processes. Signs of fat oxidation are more pronounced in fish that have been subjected to heat treatment, so a cooking test should be used to identify this defect.
According to organoleptic indicators, depending on quality, frozen fish is divided into two grades. First class fish should not be beaten, its surface should be clean, its coloring should be natural. Ice-salt and wet contact freezing fish may have a tarnished surface. Bream, carp, roach, ide, and catfish may have a red coloration as a result of hemorrhages. Fish cutting must be correct or with slight deviations. The consistency is dense, the smell (after thawing) is of fresh fish, without any discreditable signs.
The second class includes fish that is partially beaten, with bruises and minor external damage, a tarnished surface, and with subcutaneous yellowing, which can be found on cuts in the abdomen of cut fish. The consistency is weakened, but not flabby. The smell is sour in the gills and surface mucus. Fish with a slight aftertaste (after being tasted by cooking) is classified as second grade.
Specially cut frozen fish is not divided into grades; it must meet the requirements of the first grade.
The quality of frozen fish is influenced by the degree of freezing and body temperature. Freezing is considered normal if, when you tap the fish with the handle of a knife, a distinct, clear, ringing sound is heard. Thawed or frozen fish have a dull sound. Fish whose quality does not meet the requirements of the second grade is considered non-standard and is not released for retail sale.
Defrosting fish. The temperature of the fish is increased to -1-0 °C, while the ice crystals melt and a certain part of the released water is absorbed by the tissues. The completeness of absorption of the resulting moisture by the muscle fibers and the degree of restoration of the original properties of the fish depend on the thawing conditions, the depth of histological and colloidal changes that occur during freezing and subsequent storage.
The less tissue juice flows out of the fish, the juicier, tastier and more nutritious the fish. With large losses of meat juice, the fish becomes dry, fibrous and tasteless. After defrosting, the spoilage processes in fish are much more intense, so it should be immediately sent for processing. There are several defrosting methods.
Defrosting in air. The fish is placed in a chamber at a temperature of 8 to 20 ° C and a relative air humidity of 90-95%. This method is mainly used for defrosting large fish: they are laid out on racks or racks in one row and left for 20-30 hours. During this time, the surface of the fish dries out significantly, and body weight loss reaches 3%.
Defrosting with ice. Frozen fish is sprinkled with crushed ice and kept for 10 hours to 4.5 days. This method is rarely used, since it is very cumbersome and time-consuming, although the surface of the fish does not dry out and its mass does not lose.
Defrosting in a liquid medium. The fish is kept in clean fresh water in baths or a 4% solution of table salt. Defrosting is considered complete when the temperature in the thickness of the muscles reaches -1 -0°C. This method is widely used in practice; defrosting is much more intense, the weight of the fish does not decrease, and at the same time the fish is washed from mucus and impurities. The defrosting process in water takes 1 hour for small fish, no more than 6 hours for large fish, and 40-60 minutes in a salt solution.
Small and medium-sized fish are usually defrosted in water. This method is unsuitable for large fish - the meat swells greatly, becomes loose and its quality decreases. When fish defrosts in water, nutritionally valuable substances are released. Thawing in a saline solution eliminates these disadvantages, but leads to salting of the fish. In the outer layer of fish, the salt content reaches 0.6%, and in the inner layer - up to 0.3%.
When defrosting, the original properties of the fish are not restored. It is known that the proteins of fish tissues during freezing and thawing change maximally within the temperature range from +2-1 to -5 ° C. Therefore, the faster this thermal zone is overcome, the less the properties of the fish change. Therefore, in comparison with the slow one, the fast defrosting method is more preferable.
The quality of defrosted fish is assessed similarly to frozen fish.
What is "chilled fish"
This type of seafood processing does not involve complete freezing of carcasses, but bringing the meat to a temperature that does not exceed +5 ̊C. But at the same time, there is also a strict limitation on the lower temperature limit to which a carcass can be cooled - it cannot be cooled to more than -1 ̊C. Such limits are set in order to preserve the structure of meat fibers virtually unchanged.
For reference! Freezing, as well as heat treatment, affects the structure of meat in a certain way, deforming it. Because of this, it is not recommended to subject any product to more than one freeze.
Refrigeration slightly extends the shelf life of the product relative to its completely fresh state. But, not so significant in comparison with freezing seafood. Thus, chilled carcasses remain fresh and edible according to GOST for an average of 10 days. But, the maximum storage period for this type of pre-sale processing is 12 days. Such time limits are indicated due to the fact that the bacteria that provoke the decay process do not die - their vital activity only slows down.
How is cold treatment carried out?
There are several methods for cooling fish. The shelf life will depend on which method the suppliers use.
For these purposes, ice, sea water brought to low temperatures, or the same brine are used.
Most often, water is used, which is in a solid state of aggregation. In simple words - ice. It can be in the form of large pieces or finely crushed. Manufacturers of fish products use both natural and artificial.
The following types of hard water are distinguished, which are used to increase the shelf life of chilled fish:
- snow ice;
- with the addition of antibiotics (most often biomycin);
- using antiseptics (hydrogen peroxide, sodium hypochlorite and others).
Features of cutting some types of fish
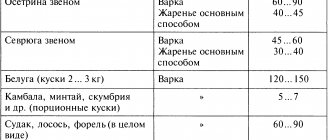
The shelf life of chilled fish and technical conditions depend on the type of aquatic inhabitants of rivers, seas and oceans.
How is gutting done?
- During this procedure, perches remain without gills. But they, like cod fish, leave behind milt and underdeveloped eggs.
- Haddock, sea bass, greenling, pollock, cod can be left with a swim bladder and ichor.
- Cod species are cleaned from the abdominal cavity along with the fins located on the peritoneum. The fish can be cut down from the anus by another two centimeters.
- Sturgeon fish are completely bled, decapitated and gutted. The exception is sterlet.
- Flounder fish have their heads cut off and their internal organs removed. You can leave the milk, caviar and kidneys.
- Salmon can be supplied either completely gutted or whole.
- Large catfish must be gutted, as well as large pike.
- The body temperature of the carcass should be from minus one to plus five degrees.
The shelf life and quality requirements for storage conditions of chilled fish undoubtedly affect the freshness of the product. Let's consider what organoleptic signs can be used to say that the fish is fresh or, conversely, that you should refuse to purchase such a product.